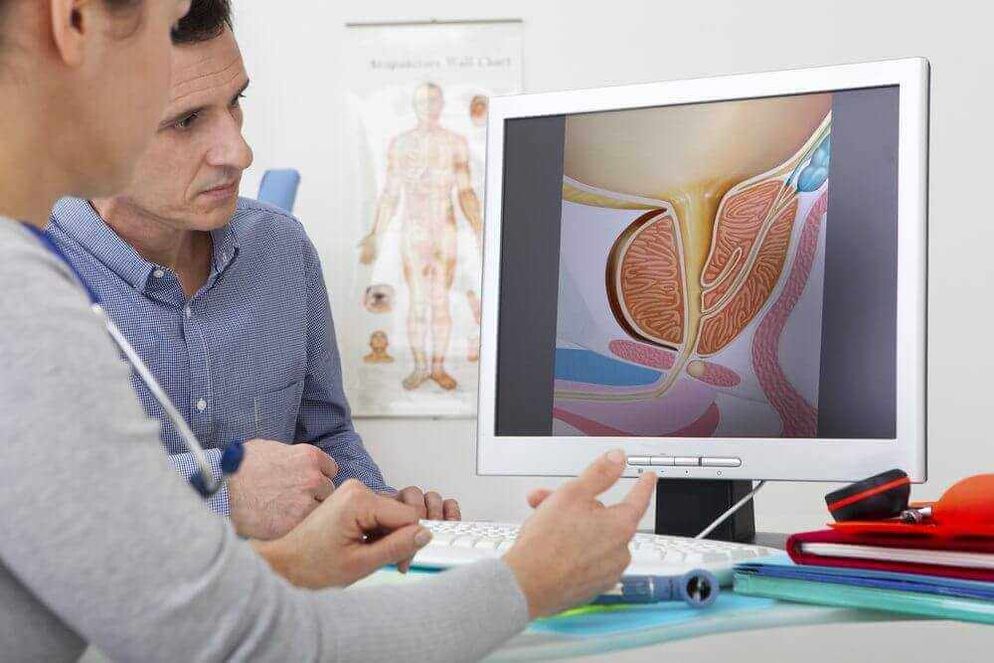
The most common urological condition advised by urologists for men over 45 is prostate adenoma. The presence of this pathology greatly reduces the quality of life of men. One of the most likely consequences of the pathological process is the degeneration of benign prostatic hyperplasia into a malignant tumor.
To combat prostate tumors, surgical and medical treatments are used. The most effective drugs or surgical interventions are selected by the hospital specialist taking into account the stage of the disease, the patient's general condition and age, as well as the presence of exacerbationsattached. The surgical clinic has created comfortable conditions for patients to treat.

The reasons for the development of the disease
The appearance of an adenoma is often associated with age-related changes in the prostate gland, namely a change in its structure and an increase in size. As a result of such changes, the urethra, which is located in the thickness of the prostate gland, is gradually compressed and disorders occur during urination.
Prostate tumors in men develop due to hormonal changes in the body associated with age-related changes. Testosterone levels (male hormones) decrease with age, while levels of female sex hormones (estrogen), by contrast, increase. This phenomenon is called male menopause.
Prostate adenoma development may be caused by the following risk factors:
- According to the age of the patient - an extremely enlarged prostate gland is rarely found in men under the age of forty, and after the age of sixty, it is diagnosed in almost every second;
- Hereditary predisposition - if the prostate adenoma is diagnosed in people with close blood ties to a man, he is at a great risk of inheriting the disease in adulthood;
- Diabetes, cardiovascular disease - a benign tumor (adenoma) of the prostate gland can be caused not only by these diseases but also from the harmful effects of drugs on their treatment (for example, beta blockers);
- Wrong lifestyle - increased risk of developing prostate adenoma in obese men, inadequate physical activity.
The symptoms
Prostate tumors can be suspected when a man develops the following symptoms, most typical for this disease:
- increased need to urinate;
- the appearance of a need to stretch the abdominal muscles to urinate;
- presence of painful, burning sensation, slow flow of urine;
- discomfort and inadequate bladder emptying;
- increase the duration of the urination process.
Prostate tumors not only lead to a decrease in the quality of life for men, but also cause an acute urinary retention that requires them to use surgical methods for treatment. To avoid surgery, many patients take prostate adenoma drugs, which eliminate symptoms and restore normal prostate function. However, only a qualified specialist can recommend the best treatment for prostatitis and prostate adenoma. It is necessary to contact him when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
Treatment for prostate tumors is individualized. The drug for the treatment of prostate tumors, the dosage and duration of use is prescribed by the healthcare practitioner. Arbitrarily taking remedies for prostatitis and prostate adenoma are not only ineffective but also dangerous. Due to the presence of a number of "individual" chronic diseases in elderly men, the choice of drugs for the treatment of prostate adenoma in the elderly takes into account the comorbidities.
The stages of the disease
Adenoma of the prostate gland is characterized by gradual development, which can be divided into three stages.
- The first stage of the disease progresses with minimal urinary disorders. The frequency of urination may increase slightly, especially at night, and the amount of urine is slow. The first phase can last from a year to 12 years or more.
- The second stage of prostate adenoma is characterized by more pronounced urination disorders: interrupted urine flow, a need to squeeze during urination, and a feeling of an incomplete bladder. Residual urine in the bladder and urinary tract causes inflammation, accompanied by pain, burning when urinating, pain in the lower back and pubic area.
- The third stage is characterized by cyclic or continuous incontinence, forcing the patient to use a urine bag.
Complications
In some men, prostate tumors do not deteriorate their quality of life and progress without complications. However, in some cases, the disease can cause the following negative consequences:
- Acute urinary retention - it is characterized by an inability to suddenly empty the bladder and pain in the posterior upper region. With such a condition, the patient needs emergency care with a catheter or minor surgery;
- The appearance of infection in the urinary tract - stagnation of urine, which facilitates the reproduction of the pathogen, leads to the development of cystitis and pyelonephritis;
- The formation of stones in the bladder is also a result of urine retention;
- Damage to the bladder - the bladder is irregularly empty, it stretches, forming protrusions (pockets) in the walls of the organ, in which urine is stagnant;
- Kidney damage - an increase in pressure in the ureter and bladder has a direct effect on the kidneys, as a result of which kidney failure develops.
Prostate tumor and potency
Adenoma of the prostate gland and the effect is closely related to each other. Adenoma disrupts the structure of the tissues of the gland, which in turn leads to damage to another organ, no less important - the testicles, which is responsible for androgen production. Thus, prostate adenoma can be the cause of impotence, requiring long-term and complicated treatment.
Diagnose
A simple and effective way for a preliminary diagnosis is to log a patient's urination with the determination of quantitative and qualitative parameters: volume of excreted urine, volume characteristics, urination, night sub. The main method of physical examination to suspect prostate adenoma is a digital rectal examination of the prostate gland to detect its enlargement and rule out several other conditions.
Prostate tumor diagnosis in the hospital is done by the following test methods and instruments:
- General blood and urine tests;
- Biochemical blood test for signs of kidney condition, urea and creatinine levels;
- PSA test (to rule out prostate cancer);
- Ultrasound examination of the rectum (ultrasound);
- Urine flow measurement (to determine the flow rate of urine);
- Determination of remaining urine volume (using ultrasound);
- Pelvic electromyography;
- Urethra endoscopy;
- Examination of the urinary tract.
Treatment
Treatment for prostate tumors is aimed at relieving symptoms of the lower urinary tract, improving the patient's quality of life and preventing the development of complications of the disease. Patients with mild symptoms that do not deteriorate their quality of life are often monitored by urologists and recommendations on how to prevent prostate tumor growth. During this period, attention focuses on non-pharmacological treatment. The above methods can be an adjunct to conservative treatment, that is, taking the following medications:
- Alpha blockers (Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin);
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Finasteride);
- Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (Sildenafil);
- Combination of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and alpha blockers;
- Muscarinic receptor blockers or M anticholinergic drugs.
For patients with end-stage prostate adenoma, surgical treatment is recommended, which can be done by a number of methods: vasectomy, prostatectomy and prostatectomy.
There are a number of indications for the use of surgical treatment:
- Recurrent urinary retention;
- Kidney failure caused by prostate adenoma;
- Bladder stones;
- Recurrent urinary tract infection;
- Recurrent hematuria.
In addition, surgical intervention is necessary for the patient in the absence of efficacy from drug therapy.
During conservative therapy or in the postoperative period, patients should be under constant medical supervision with standard studies (urine flow rate determination, ultrasound, PSA level analysis).
Drug
There is a certain program under which specific drugs are prescribed for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma. High therapeutic effect is achieved by using drugs of the alpha-reductase inhibitor group and alpha blockers. These drugs to treat prostate adenomas in men eliminate the main symptoms of the disease, as well as restore full urination.
Which pills are the most effective and widely used for prostate tumors? This list is topped by alpha1-adrenergic receptor blockers. Additionally, this list includes 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, vitamins and minerals.
The complexities of drug therapy are not just drugs. In the case of prostate adenoma, conservative treatment can be supplemented with bioactive additives - functional foods, which enhance the therapeutic effect of the drug and ensure a quick recovery. Some of them contain zinc. This macronutrient is directly involved in the spermatogenesis and synthesis of testosterone. Plant phytosterols normalize urination.
Treatment with drugs belonging to the alpha1 receptor antagonist group
These drugs for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenomas relax the smooth muscles of the urinary system and improve the flow of urine. Tamsulosin of the same active ingredient, which is part of other drugs (Alfuzosin, Silodosin, etc. ), is a highly selective drug that has a selective effect on the alpha1-adrenergic receptors of the prostate muscle. , Prostate. urethra and bladder. Due to a decrease in muscle tone is facilitated the process of passing out and excreting urine. Tamsulosin, like all select drugs, has some minimal side effects, has no effect on vascular tone and can be prescribed for patients with chronic hypertension.
Alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists must be used on an ongoing basis to gradually reduce irritation and blockage in prostate adenomas. Tamsulosin drug in the treatment of prostate tumors is very worthy of priority in the prescription of urologists.
The tablet form of the drug is considered to be more advanced, because because the release of tamsulosin is controlled, the active substance is present in the body at constant concentrations. The drug enters the bloodstream evenly, thereby reducing the likelihood of developing a major side effect of the drug in the adrenergic blocker group - a decrease in blood pressure.
An equally effective drug with the active ingredient tamsulosin is Urorek. The use of this drug is not associated with the following undesirable effects: orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, increased frequency of angina attacks in patients with coronary artery disease, so it can be prescribed for men with medical conditions. heart. Well-selected dosages and adherence to all rules of use of alpha-blockers allow a good therapeutic effect with virtually no side effects.
Drugs belonging to the group of reducing enzyme inhibitors (blockers)
Drugs of this pharmacological group (Finasteride, Dutasteride) help to reduce the amount of urine flowing out, and thus, eliminate the main symptoms of the disease. Stable therapeutic effects occur within two to three weeks after starting therapy. All symptoms were completely resolved after three months. According to the results of clinical studies, the maximum effect is achieved after six months of treatment with these drugs.
Finasteride and Dutasteride are specific inhibitors of type 2 5-alpha reductase (a cellular enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone). Prostate growth in BPH is directly related to this testosterone conversion. Thanks to the 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor, the production of intravenous dihydrotestosterone is blocked and its concentration in the blood is significantly reduced.
Finasteride and Dutasteride are used for the following purposes:
- Treatment and control of prostate hyperplasia;
- Improve the flow of urine and eliminate symptoms of prostate adenoma;
- Reduces the risk of developing acute urinary retention and the need for surgery.
Finasteride and Dutasteride have a pronounced anti-male hormone effect, ie helping to reduce the concentration of male hormones in the blood. In addition, these drugs have a teratogenic effect so extreme caution must be exercised. With the help of modern drugs, it is possible to stop the growth of the prostate gland and prevent the need for surgical treatment.
Antispasmodic and analgesic drugs for the exacerbation of the disease
The main purpose of antispasmodic and analgesic drugs during the exacerbation of prostate adenoma is to alleviate the patient's general condition and eliminate pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, ibuprofen) have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. They help combat pain not only that arise when urinating, but also with constant pain in the groin and perineum. Thanks to the action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the inflammatory process decreases, the swelling of the prostate decreases, the body temperature is normalized and unpleasant symptoms are also eliminated.
Non-opioid pain relievers, produced in the form of tablets or suppositories, help relieve pain syndrome during an exacerbation of prostate adenoma. The most available of these is Metamizole sodium. However, this drug is indicated for single use only, as it can only act on mild pain syndrome. In addition, pain relievers with lidocaine, benzocaine, anesthetics and novocaine (Ikhtammol, Benzocaine, Tribenoside + Lidocaine) are effective.
Vitamin E 400
Tocopherol acetate or vitamin E is often included in the complex treatment of prostate adenoma as an antioxidant, radiation protector and an irreplaceable bond during reproduction. Vitamin E in a dose of 400 mg urologist prescribes for patients with erectile dysfunction and spermatogenesis associated with prostate adenoma.
Treatment for a serious chronic disease such as prostate adenoma should be prescribed and monitored by a urologist. It is strictly forbidden to arbitrarily use certain drugs without consulting a doctor first because arbitrarily using drugs in this case is not only ineffective but also endangers men's health. Only a qualified specialist can tell you which medications for prostate adenoma are most effective in each case and which may have negative consequences.

Work
The hospital's urologists are proficient in classical and minimally invasive surgical interventions, applying state-of-the-art surgical methods in the treatment of prostate tumors. Each patient can choose the surgery that best suits him.
The commonly accepted standard for surgical treatment of prostate tumors is prostatectomy. High efficiency operation. After the intervention, the patient got rid of the obstruction of the way out of the bladder (urethral stenosis) and accompanying symptoms. The recovery time is short. During or after surgery may bleed, "water intoxication" syndrome of the body.
Alternative treatments for prostate tumors include the following surgical interventions:
- Place stent;
- Balloon expansion;
- Increased body temperature;
- Heat therapy;
- Ultrasound, laser and needle ablation;
- Interstitial coagulation.
After that, complications are less likely to occur, but the techniques are less effective than vasectomy in terms of effectiveness, both clinically and economically.
Prostate resection is used when the tumor has grown significantly and has problems removing it by laparoscopic resection. This is more difficult and is performed under general anesthesia. Through small incisions, the surgeon inserts special instruments into the body cavity, through which he removes the prostate adenoma. The operation is performed according to the image from the video camera, displayed on the screen. The main advantages of the intervention are the minimal amount of blood loss and the low likelihood of complications. After surgery, the patient does not need long-term rehabilitation.
When there are signs of prostate adenoma in men, doctors will use a high-tech adenoma treatment - laser burning. Intervention is performed with large tumors. Excess tissue is removed using a laser. Operation is performed through the urethra. Tumor is separated, divided into many small parts and then excreted out. The method is considered as minimally invasive. It has a number of significant advantages: it does not violate the integrity of the cavities, does not cause undue damage.
Laser steam is the destruction of an adenoma by laser steam. The urologist introduces a special device through the urethra, sends it to the tumor and acts on it clockwise with a strong blue laser. The laser's penetrating depth and shot accuracy make it possible to avoid damage to neighboring areas. Minimal invasive, blood-free, fast and effective method. Its only drawback is the inability to take tumor tissue for histological examination.
In some situations, one treatment for an inevitable prostate tumor is abdominal surgery - removal of the gland. It is performed when other methods cannot help the patient. During surgery, the surgeon uses a scalpel to reach the prostate gland and manually, using surgical instruments to remove the adenoma. As a result of surgery, there is a possibility of significant blood loss and possible development of complications. After surgery, the patient needs long-term rehabilitation.
Removal of an adenoma of the prostate gland with a glandularectomy (transectomy) involves radical removal of the hyperplastic prostate tissue through a longitudinal incision of the anterior abdominal wall and bladder. Surgery is performed at a severe stage of the disease, when the tumor is large, the bladder becomes strained due to a buildup of urine overflow and kidney failure.
The bladder is placed with a catheter first and filled with sterile furacilin solution or another substance. It was then quarantined and placed in two places on special racks, to lift the wall of the organ. The surgeon dissects the fold that has formed and opens the bladder.
Along the inner end of the catheter is installed, it identifies the area of the bladder neck and around the urethral opening appears in the field of view, 0. 5-1 cm away from it, making an incision on the membrane lining. Then, the urologist uses the finger to penetrate the thickness of the prostate gland, go between the tumor cyst and the glandular lymph nodes, and expel the waste. At the same time, with the finger of the other hand previously inserted into the patient's rectum, the doctor will bring the gland toward the anterior abdominal wall. It becomes easier to operate. Thanks to this technique, surgery time is shortened and blood loss is reduced.
The surgeon then stops the bleeding (hemostasis) of the adenoma that has been removed and stitches the bladder, leaving a thin drainage path in the wound. It is designed to clean its cavity from already formed blood clots. The catheter, inserted before the start of surgery, is not removed for 7-10 days. A new part of the urethra is formed around it instead of the prostate gland part of the urethra being removed during surgery.
Prostateectomy is one of the most traumatic of all techniques used for prostate adenoma. It is accompanied by a risk of developing the following complications:
- Bleeding cancer bed;
- Congestive pneumonia;
- Violation of the intestinal motor evacuation function, manifested by constipation.
To avoid complications, after the surgery at the hospital, the patient was activated early. The following undesirable consequences of prostatectomy may occur:
- Insufficient bladder drainage;
- Narrow neck;
- Urinary infiltrates of the tissue around the blisters;
- The formation of a "pre-bladder" (cavity left over where the prostate adenoma was removed);
- Formation of stenosis of the lumen of the urethra;
- Urinary incontinence.
This negatively affects the patient's quality of life and prolongs the recovery time for adequate urination.
The consequences of the operation are less pronounced when the intervention is performed by endoscopy. Prostate laparoscopic surgery is one of the less invasive options for surgical intervention in the prostate gland. This technique is used by the hospital urologists if the patient has a large enough prostate tumor.
If the size of the prostate gland of a patient with an adenoma does not exceed 120 cm3, the prostate gland should be removed through endoscopy. But for 10% of patients who need surgery, this option is not suitable, since the gland reaches more than 120 cm3. Do not perform laparoscopic surgery to remove prostate adenoma with urolithiasis, inguinal hernia, bladder diverticulum, lower extremity joint stickiness. In this case, the decision about the possibility of surgery is made collectively by the urologist, male doctor, abdominal surgeon and other specialists of the hospital.